How to Share Content on Multiple Social Media Platforms: A Complete Guide
Social media sharing requires connecting your accounts first and understanding platform-specific limitations. Here's how to effectively share your content:
Supported Platforms & Content Types
- Facebook (Business Pages only)
- LinkedIn (Personal profiles only)
- Tumblr
You can share:
- Blog posts
- Events
- Products
- Album tracks
- Gallery pages
Platform-Specific Limitations
Facebook:
- Only allows sharing to business pages, not personal profiles
- Requires external sharing setup
LinkedIn:
- Limited to personal profiles
- Company page sharing must be done manually
Pinterest:
- Requires feature images for blog posts and products
Tumblr:
- Supports text, image, markdown, quote, and video blocks
- Dashboard view may display blocks differently than published view
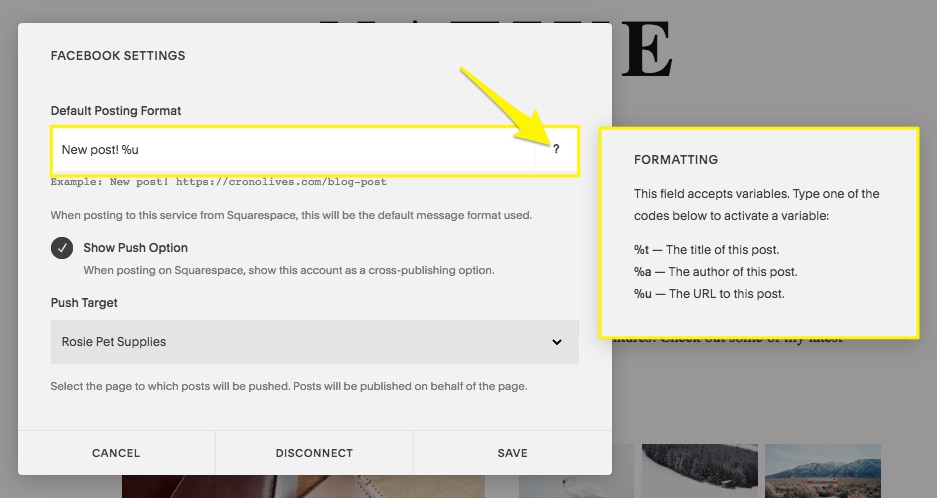
Facebook Post Settings Screen
Connecting Your Accounts
- Go to Settings > Connected Accounts
- Click Connect Account
- Select platform and login
- Enable "Show Publishing Options"
- Select sharing preferences
- Create default post format
- Save settings
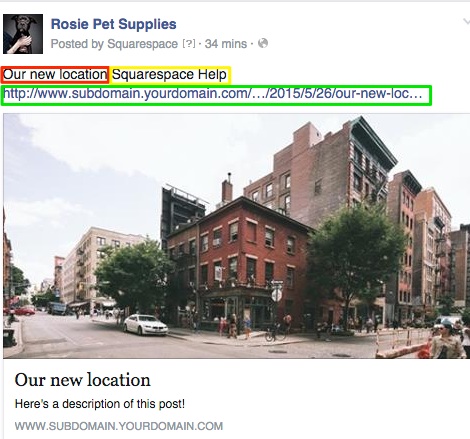
Street with Red Building
Customizing Post Formats
Use these variables in your default format:
- %t - Title
- %a - Author
- %u - URL
To Share Content:
- Access item's edit screen
- Click Share tab
- Toggle desired platforms
- Set status to Published
- Save changes
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Wrong account: Disconnect, logout, and reconnect
- Facebook issues: Check for cached information
- Pinterest problems: Verify feature images
- Tumblr display: Remember block limitations
For resharing content, use manual URL sharing as repeated automated sharing isn't supported.
Remember to regularly review your sharing settings and update connected accounts as needed for optimal performance.
Related Articles

How to Choose and Customize Your Squarespace Template - A Complete Guide